Comments of the International Center for Law & Economics on Proposed Changes to the Premerger Notification Rules
I. Introduction
We appreciate the opportunity to comment on the proposed changes to the premerger notification rules recently published by the Federal Trade Commission (“FTC”), with the concurrence of the Assistant Attorney General of the Antitrust Division of the U.S. Department of Justice (“DOJ” or “Division”).[1]
Merger law in the United States has largely tracked developing economic theory.[2] This approach has tended to reject structural presumptions about a merger’s likely effects on competition and consumers (understanding, that is, that “big” is not necessarily “bad”). It encourages weighing the potential anticompetitive effects of a transaction against its potential procompetitive efficiencies.
That trend in enforcement and jurisprudence notwithstanding, current leadership at the agencies has signaled a more aggressive approach to enforcement, dismissing likely efficiencies and other merger benefits. For instance, the Chair of the FTC has argued that Section 7 of the Clayton Act:
is a broad mandate aimed at prohibiting mergers even when they do not constitute monopolization and even when their tendency to lessen competition is not certain. . . . [E]ven if a merger does create efficiencies, the statute provides no basis for permitting the merger if it nevertheless lessens competition.[3]
The substantive changes to both the merger guidelines and the premerger notification form relate to this goal of more aggressive merger enforcement. As we explain below, while certain changes are required by statutory amendments to the Clayton Act, many of the proposed amendments would be both unnecessary and inappropriately burdensome and costly. Collectively, they would exceed the agencies’ statutory authority, under Section 7A of the Clayton Act,[4] to require the production of “such documentary material and information relevant to a proposed acquisition as is necessary and appropriate … to determine whether such acquisition may, if consummated, violate the antitrust laws.”[5]
While further research, enforcement experience, and legal precedent might develop such that certain additional information would reasonably be required of all filers, the agencies have not presented the requisite developments in the NPRM or, to the best of our knowledge, elsewhere. Such developments should, at least, precede the imposition of substantial new filing requirements. The HSR regulations and form are not supposed to be a substitute for, e.g., the FTC’s study authority under Section 6(b) of the FTC Act.[6]
The scope of the NPRM and the diversity of additional information that filers would be required to produce should the proposals be adopted together raise a fundamental question: how will the new requirements materially improve merger screening? Are the agencies often or systematically clearing anticompetitive mergers because of information not included in initial filings, and that staff cannot glean via, e.g., follow-up queries to the parties, voluntary requests, pull-and-refiles, and second requests? Would such mergers fail to clear under the proposed filing requirements? Answers to these and other questions, which nowhere appear in the NPRM, are needed to maintain that these changes are necessary and appropriate, given the other means by which the agencies can obtain information to inform premerger screening (such as through second requests).
Section I offers some background concerning the purpose of the HSR form and filing requirements, and on the changes that have been proposed. Section IV provides a brief discussion of the proposed changes that are necessary or otherwise reasonable. Section v discusses the changes that are problematic. These would increase compliance costs for merging parties generally, with disproportionate impact on small and first-time filers; they would impose additional burdens on agency staff; yet it is unlikely that they would provide countervailing benefits to competition and consumers.
II. Background: Merger Enforcement and the HSR Premerger Notification Form?
At the outset, we note that the proposed changes to the premerger notification rules (“NPRM”) were closely followed by the agencies’ publication of new draft merger guidelines.[7] That makes some sense, as the two are closely intertwined. Section 7 of the Clayton Act prohibits mergers where the effect “may be substantially to lessen competition, or to tend to create a monopoly.”[8] In 1976, Congress enacted the Hart–Scott–Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act (“HSR Act”) to facilitate enforcement of Section 7. Specifically, the HSR Act created a premerger notification mandate, under which transactions exceeding certain market share or value thresholds must be reported to the DOJ and FTC at least 30 days prior to closing.[9] The agencies use these 30 days to screen proposed large transactions and to determine whether further scrutiny is needed as to whether a transaction might violate the Clayton Act.[10]
The premerger notification process is a congressionally created mechanism that requires parties to relatively large transactions to provide the agencies with notice of, and opportunity to go to court to enjoin, those transactions before they close. Initial filings are a critical basis on which agency staff can screen proposed mergers effectively, although, of course, the production required by the HSR form itself is far from the only source of information available to staff screening mergers prior to closing.
Reviewing staff can—and routinely do—ask merger-specific follow-up questions during that initial 30-day period, in addition to consulting third parties and other sources of information. The agencies can then issue a request for additional information, called a second request, to the parties to get further details about a transaction and to decide whether to seek to enjoin the merger from proceeding.[11] With that second request, the reviewing agency may extend the screening period for an additional 30 days.[12] In the interim—often prompted by additional staff questions—parties may elect to “pull and refile,” which restarts the initial 30-day clock and permits additional information gathering by the staff in advance of a decision regarding whether to issue a second request.
The HSR premerger notification requirements address a basic problem of antitrust law: you can’t “unscramble an egg.”[13] Once a merger is finalized, businesses begin intermingling their operations, personnel, finances, business plans, trade secrets, and intellectual property in various ways. The larger the firms—or the more complex the integration or consolidation—the more difficult it becomes to undo (or “unwind”) a consummated merger. Premerger notification creates an opportunity for the antitrust agencies to identify and pause pending mergers, in order to allow for more thoroughgoing investigation of their potential competitive effects before any eggs have been scrambled.
When the HSR Act was adopted, it was expected that only 150 or so transactions each year would be large enough to trigger review.[14] In time, that estimate proved to be off by more than an order of magnitude; in recent years, more than that many transactions are notified each month.[15] The effect has largely been to transition merger law in the United States from an ex post enforcement-based regime to an ex ante regulatory regime.[16]
Despite this change, the premerger notification regime is generally viewed as successful. [17] This is because the program has been designed and managed with the understanding that it is meant only to identify mergers that are likely problematic; and, conversely, that it is meant not to impede the vast majority of mergers that are unlikely to be problematic (but likely procompetitive or benign). [18] Combined with the merger guidelines—which have (in the past) provided clear guidance on how the agencies will review materials submitted as part of the premerger notification process—the HSR Act’s premerger notification process has created a robust and relatively low-burden system. This system enables business and antitrust agencies alike to identify problematic transactions, while allowing most deals to proceed with minimal cost or delay. The balance is captured in a December 2020 advance notice of proposed rulemaking that contemplated other premerger-filing amendments: “[t]he Agencies have a strong interest in receiving HSR filings that contain enough information to conduct a preliminary assessment of whether the proposed transaction presents competition concerns, while at the same time not receiving filings related to acquisitions that are very unlikely to raise competition concerns.”[19]
A very large majority of reported mergers are consummated without challenge or allegation of likely anticompetitive effects. For example, the agencies reported challenging only 32 of the 3,520 transactions reported in fiscal year 2021; that is, 0.009%.[20] Across the 10-year period from fiscal years 2012-2021 (inclusive), in the vast majority of cases, neither agency even issued a second request. It is reported that DOJ issued second requests in frequencies ranging from 0.7% to a high of 2.1% in 2012, while FTC issued second requests in 1.4% to 1.9% of investigations.[21]
The agencies’ multiple opportunities to receive and request information prior to the consummation of a transaction, along with the relative infrequency with which additional information is requested, or with which transactions are challenged, are the context in which to ask whether it is “necessary and appropriate” to require the production of certain information with the initial HSR filing. As a simple example, if roughly 2% of noticed transactions receive a second request, the compliance burden of requesting information of all firms as part of the premerger notification process is roughly 50 times greater than it would be if the information were requested only with a second request.[22] And that burden is one imposed on both reviewing staff and filers.
III. Direct Costs
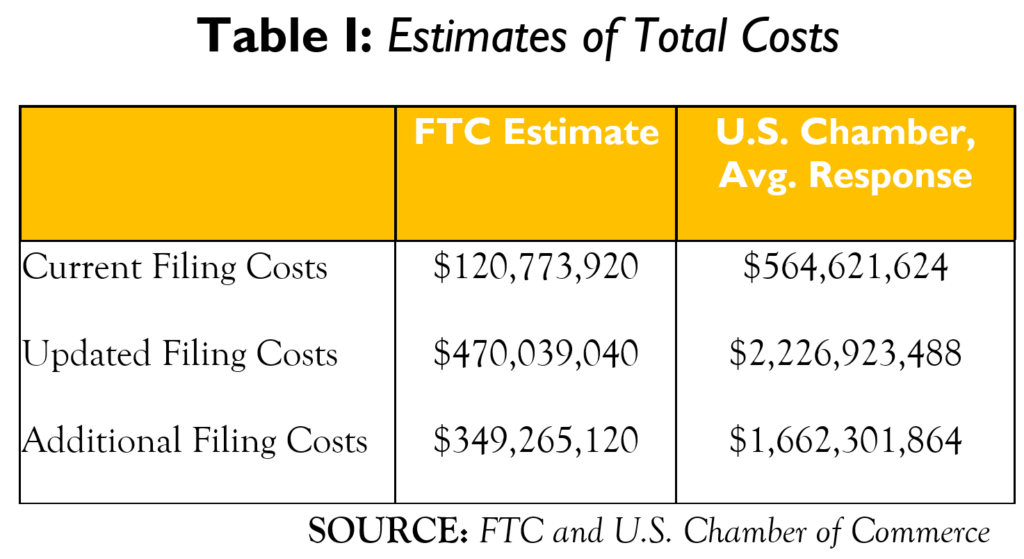
From the outset, it is important to understand that the proposed amendments are anything but costless. Estimates suggest the new rules will lead to somewhere between $350 million and $2.23 billion in additional annual compliance costs. Not only will these additional costs deter firms, at the margin, from filing—and hence from merging—but they will also be passed on to consumers (at least in part) when firms do. The substantial costs that would be imposed by many of the proposed requirements raises the bar for deeming such amendments appropriate.
Even the FTC estimates a massive increase in compliance costs of approximately $350 million, to more than $470 million per year. But that estimate is likely a serious underestimate, as it is based on, among other things, an unscientific “estimate” of the time involved and a dated assumption about the average hourly costs imposed on filers’ senior executives and firms’ counsel.
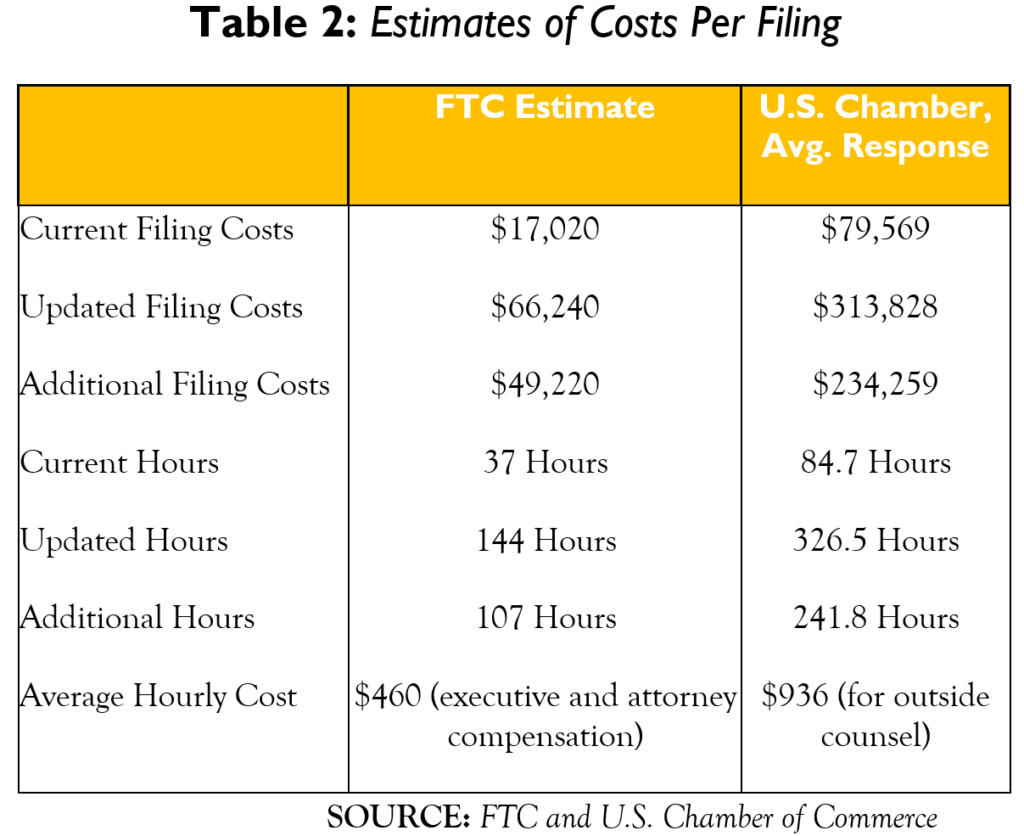
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce conducted “a survey of 70 antitrust practitioners asking them questions about the proposed revisions to the HSR merger form and the new draft merger guides.”[23] Based on average answers from the survey respondents, the new rules would increase compliance costs by $1.66 billion, almost five times the FTC’s $350 million estimate. For the current rules, the average survey response puts the cost of compliance at $79,569.[24] Assuming there are 7,096 filings (as the FTC projects for FY 23), the total cost under the current rules would be $565 million. Under the new rules, the average survey response estimates the expected cost of compliance to be $313,828 per transaction, for a total cost of $2.23 billion.[25] The relevant total costs for all filing are summarized in Table 1. Table 2 presents the numbers on a per-filing basis.
Even if we assume the U.S. Chamber of Commerce’s survey was biased toward practitioners who work on more complex and costly transactions, it is dramatically higher than the FTC’s estimate. The FTC estimates that 45% of filings have overlaps.[26] For simplicity, assume survey respondents work only on overlaps and the remaining 55% of filings require no extra work.[27] Even with these extreme assumptions, the amendments would increase the cost of filing by nearly $750 million—more than double the FTC’s estimate.
On any reasonable estimate, the amendments are likely to impose substantial new costs on all filers and may have significant effects on firms’ incentives to merge—and important consequences for consumers when they do. They may also have an outsize impact on relatively small filers. The merits of these amendments should thus be carefully considered against their substantial and widespread costs.
IV. Required and Reasonable Changes to the Reporting Requirements
The HSR form has been amended many times since 1976.[28] Some of the amendments have been minor or even ministerial, and many—not all—have been required by statutory amendments to the pertinent provisions of the Clayton Act.[29] For example, revised reporting thresholds were noticed in January 2023,[30] January 2022,[31] and February 2021,[32] and the commission published an advance notice of proposed rulemaking regarding various potential changes in December 2020.[33]
Consistent with past practice, some of the amendments proposed in the NPRM implement 2022 amendments to pertinent provisions of the Clayton Act, while others appear to streamline or clarify reporting requirements. That is, some of the proposed changes are necessary and others appear at least appropriate.
First, as noted in the NPRM, certain proposed amendments implement 2022 statutory amendments imposed by the Merger Filing Fee Modernization Act of 2022.[34] For example, the 2022 statutory amendments require the disclosure of subsidies from nations or entities that Congress has identified as “foreign entities of concern” and correspondingly requires that the agencies collect such information with premerger filings, and that they promulgate regulations to that effect.[35] The NPRM’s proposed changes to Part 801.1 of the HSR rules appears to be a reasonable implementation of 2022 congressional charge.
Second, the NPRM’s proposal to amend Part 803 to require electronic filing[36] will likely be salutary, especially with the successful implementation of an e-filing platform that, according to the NPRM, is under development.[37] As observed in the NPRM, the agencies have been accepting electronic HSR filings since March 2020.[38] Many filers have taken advantage of the electronic-filing option since then. Furthermore, premerger screening by staff can be carried out more efficiently with electronic documents. Given the increased digitization of pertinent documents across the economy, it is reasonable to assume that the formal routinization of electronic filing will streamline both premerger filing and the screening of filings by agency staff. The extent to which this will make premerger filing and screening more efficient depends on the successful implementation of an e-filing platform. If successful, the benefits should be substantial.
V. Problematic Changes to the Filing Rules Are Not Justified by the NPRM or Otherwise
While several of the NPRM’s proposed changes appear to be reasonable attempts to implement new statutory mandates or, as in the case of electronic filing, pragmatic initiatives to update and streamline the filing and review processes, others appear cumbersome, costly, and unnecessary or, at best, substantially unjustified by the NPRM or other available evidence.
For example, Parts 4(c) and 4(d) of the current premerger notification form require merging parties to provide copies of “all studies, surveys, analyses and reports which were prepared . . . for the purpose of evaluating or analyzing the acquisition” and “all Confidential Information Memoranda . . . that specifically relate to the sale.”[39] The proposed changes would require an additional “narrative that would identify and explain each strategic rationale for the transaction.”[40] That narrative would not have been created in the ordinary course of business, and likely not even in the context of contemplating a transaction. Creating it would come at a real cost, in terms of billable hours and executives’ time. This might imply a requirement that the parties prepare a reply brief to a potential future antitrust challenge to the transaction, without the benefit of knowing the specific arguments that the agencies would make against it.
In brief, the changes proposed in the NPRM would force parties to submit far more information than the HSR rules now require. Much of this information appears to be of, at best, peripheral value to screening mergers under the Clayton Act. The result is that the NPRM would greatly increase the burden placed on all merging parties, while apparently offering little countervailing value to competition and consumers, or even to the staff charged with premerger screening. Some have even suggested this may be the purpose of the changes: “killing deals softly”[41] by making mergers more costly in an effort to deter at least some of them, including even some that ultimately would be cleared by agencies and courts.
A. Non-Horizontal Information
The NPRM would require both filing entities to submit considerable additional material about supply and other non-horizontal relationships between the parties, including both formal agreements, such as supply, distribution, purchase, and franchise agreements,[42] and a “supply relationships narrative section that would require each filing person to provide information about existing or potential vertical, or supply, relationships between the filing persons.”[43] The latter type of information would not likely be documented in the ordinary course of business.
The NPRM acknowledges that “this will increase the burden on filers whose transaction involves existing supply relationships or who supply or purchase from companies that compete with the other filing party.”[44] The NPRM also acknowledges that 2001 amendments to the HSR rules removed some additional vertical information that had been required “because the type of information collected did not prove useful enough to the Agencies as a screen for potential non-horizontal relationships to justify the burden of providing it at that time.”[45] The extra burden is now supposed to be justified, however, as “it would allow them to quickly identify those transactions that raise concerns about non-horizontal competitive effects.”[46]
The basis of the commission’s claim about a newfound utility for such required production is unclear. There remains the basic question of how the new requirements will materially improve merger screening. The agencies do not offer any evidence to suggest they often or systematically clear anticompetitive mergers because of information that is not included in initial filings, that staff cannot obtain via follow-up queries to the parties, voluntary requests, pull-and-refiles, and second requests, etc. In other words, there is little to suggest that many mergers would be challenged, but for the supposed lacunae in the HSR requirements.
It is worth recalling, in that regard, that a “second request” extends the initial 30-day screening period by an additional 30 days, and that Section 7A of the Clayton Act affords the agencies considerable discretion in determining “ all the information and documentary material required to be submitted pursuant to such a request.”[47] That is, the agencies have ample opportunity to obtain necessary documents that are not included in the initial premerger notification.
When the draft merger guidelines were issued, an accompanying statement by FTC Commissioner Alvaro M. Bedoya, joined by Chair Lina Khan and Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter, also addressed the question of what is missing from the extant filing requirements—i.e., what missing information impedes merger screening, to the detriment of competition and consumers? Addressing “periods of high merger activity” generally, and mergers by large tech firms specifically, the statement argues that a:
lack of relevant information is especially problematic during periods of high merger activity . . . The Commission’s recent 6(b) inquiry into unreported acquisitions by Apple, Amazon, Facebook (now Meta), Google, and Microsoft during 2010-2019 also highlighted the importance of collecting more information on the firm’s history of acquisitions, including non-horizontal and small prior acquisitions. The study captured how these firms structured acquisitions, the sectors they had identified as strategically important for acquisitions, and how these acquisitions figured into the companies’ overall business strategies.[48]
Of course, small or non-horizontal mergers might be competitively significant under particular facts and circumstances. But the study in question does not find, or even suggest, that such transactions have been typically, frequently, or in any instance anticompetitive, much less that the NPRM’s proposed changes would have allowed the staff to spot such anticompetitive mergers before they were consummated. Indeed, the study does not appear to address at all the question of whether any mergers of interest were anticompetitive. And the report expressly states that it “does not make recommendations or conclusions regarding the HSR thresholds.”[49]
A recently published paper by Ginger Zhe Jin (former director of the FTC’s Bureau of Economics), Mario Leccese, and Liad Wagman (formerly a senior economic and technology advisor in the FTC’s Office of Policy Planning who, in that capacity, played a leading role in conducting the above 6(b) study) is at least somewhat in tension with the commissioner’s representation of the study.[50] The paper finds, among other things, that “GAFAM acquisitions are less concentrated across tech categories than other top acquirer groups,” and that “[o]verall, we find that technology acquisitions do not shield GAFAM from competition, at least not from other GAFAM members or other firms that acquire in the same categories.”[51]
To be sure, neither the FTC study nor the related—more thorough—investigation by Jin, Leccese, and Wagman, demonstrates that none of the mergers in question had anticompetitive consequences. They do, however, sharpen the question of the agencies’ basis—if any—for requiring considerable additional information. In brief, the NPRM presents no evidence to contradict or reverse the 2021 determination that the screening utility of such additional non-horizontal information did not justify the burden it imposed. And that is a burden on both filing parties and reviewing staff.
B. Labor Information
The NPRM proposes to require the production of material for “a new Labor Markets section” comprising considerable information on employees of the merging parties—information not previously identified under the HSR regulations.[52] The likely utility of this information is unclear.
1. Overlaps in quasi-labor markets
Both the acquiring party and the target would be required to gather information on their employees in each of five standard occupational classification (SOC) categories, with occupations defined by six-digit SOC codes.[53] For each of the five largest such groups of employees, both filers would be required to identify any SOC codes in which they both employ workers, as well as any overlap in employees’ commuting zones and the total number of employees within each commuting zone.[54]
The NPRM acknowledges that neither six-digit SOC codes (developed by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics) nor commuting zones (as determined by the U.S. Agriculture Department’s Economic Research Service) were developed to facilitate competition analysis generally, or merger screening specifically. Thus, they do not determine the product/labor markets or geographic markets in which labor competition might be impeded. The NPRM nonetheless suggests that such information will serve as a useful “screen” or “initial proxy for labor issues while balancing the burden on filers by limiting the request to their five largest categories of workers.”[55]
Given the systematic misfit between the proposed “Labor Markets” section and any actual labor markets, given the agencies lack of experience in analyzing the local labor-market effects of proposed mergers, and given the hard questions of when or under what conditions such labor-market effects might be both material and unlikely to covary with product-market effects, we suggest that the screening utility of the new information remains unclear.
In addition, the NPRM seeks comment on the question of whether such information would be costly to collect. In that regard, it is worth noting that firms are highly unlikely to collect or maintain this employee information in the manner proposed in the ordinary course of business. Hence, the gathering of such information might represent a substantial new burden on HSR filers. Compiling such information is not what is ordinarily understood to be “production” in the discovery context, and it would be a burden with unclear benefits to competition and consumers.
Of course, certain labor-market information may be pertinent to the analysis of certain mergers. But if it is unclear what new labor information would be useful, reasonable, and necessary to merger screening, then further research—as well as further enforcement experience—is warranted to determine the scope of such information before the imposition of costly regulations. As noted in the introduction to these comments, the HSR rules and form are not supposed to be substitutes for enforcement experience or, e.g., the FTC’s study authority under Section 6(b) of the FTC Act.
2. Worker and workplace-safety information
In addition, both filing firms would be required to identify various “worker and workplace safety information.”[56] Specifically, for the five years immediately preceding the filing:
…any penalties or findings issued against the filing person by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Wage and Hour Division (WHD), the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB), or the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the last five years and/or any pending WHD, NLRB, or OSHA matters. For each identified penalty or finding, provide (1) the decision or issuance date, (2) the case number, (3) the JD number (for NLRB only), and (4) a description of the penalty and/or finding.[57]
The purported rationale for this requirement appears strained. The NPRM suggests that “[i]f a firm has a history of labor law violations, it may be indicative of a concentrated labor market where workers do not have the ability to easily find another job.”[58] That is not impossible, but it does not seem likely, and the agencies provide no basis on which to think that the signaling value of such information would be significant.
According to the Department of Labor’s Occupational Safety and Health Administration (“OSHA”), these types of violations occur most often in the construction and general-industry sectors. Of the 10 most frequently cited OSHA violations, five are in the construction sector—not commonly a highly concentrated one—and five are in “general industry.”[59] We are not aware of any literature showing a significant correlation between such violations and highly concentrated product markets (or even industries), or with highly concentrated labor markets, much less with anticompetitive mergers, and the NPRM does not cite any.
VI. The Limits of Reasonable and Necessary Filing Requirements
As described briefly in the background section of these comments above, certain aspects of the premerger notification process are specified in the statute, while others are left to agency implementation and discretion. Section 7A(a) of the Clayton Act specifies the transactions for which notice must be given.[60] And Subsections (b)(1) and (e)(2) specify the duration of the initial waiting period, as well as that for second requests.[61] But other aspects of the premerger notification process are delegated to the agencies to develop by rule, requiring that:
The Federal Trade Commission, with the concurrence of the [DOJ] and by rule in accordance with section 553 of title 5, consistent with the purposes of this section—shall require that the notification required under subsection (a) be in such form and contain such documentary material and information relevant to a proposed acquisition as is necessary and appropriate to enable the Federal Trade Commission and the Assistant Attorney General to determine whether such acquisition may, if consummated, violate the antitrust laws[.][62]
Implementation of premerger notification is subject to the rulemaking process outlined in Section 553 of the APA.[63] This process requires, for instance, putting out a notice of proposed rulemaking, soliciting comments, and publishing final rules that explain their basis and respond to substantial comments.[64] Rules adopted through this process carry the force of law and are binding on parties and the courts. A challenge to such rules would need to show that the agency had been arbitrary or capricious in adopting them,[65] or that there were defects in the rulemaking process such as a failure to respond to significant comments or adoption of final rules that were not a “logical outgrowth” of those contained in the proposed changes to the rules.[66]
As described above, the proposed changes to the premerger notification requirements are significant. Indeed, the FTC’s own estimate of the costs of the proposal exceeds the entire 2023 antitrust budget for the FTC and DOJ combined.[67] More substantively, the proposed changes to the premerger notification form would impose significant costs on firms; and some would appear prejudicial.
A particular area of substantial change discussed above has to do with the production of considerable employee or labor-regulation information, such as the parties’ history of OSHA complaints.[68] This, again, would require compiling information firms are not likely to gather and maintain in the ordinary course of business. This concern is even more severe, because the agencies’ concern with the local labor-market implications of mergers—including mergers that may have national geographic markets from a product perspective—is of recent provenance.[69] As we discussed above, the antitrust relevance of information such as OSHA complaints is dubious or, at least, unclear. It may be that the agencies will, in time, develop sufficient experience with these aspects of merger cases to justify labor-related changes to the HSR rules. At present, however, the information proposed to be required seems better suited to a research proposal—perhaps under the FTC’s study authority under Section 6(b) of the FTC Act—than it does to a regulatory requirement.
The changes to the premerger notification requirements would be significant. Perhaps the simplest metric to capture the scope of these changes is the FTC’s own estimate of compliance costs. With the current HSR premerger notification form, the FTC estimates that aggregate annual HSR compliance costs are approximately $120 million. Under the new requirements, the FTC estimates this would increase by approximately $350 million, to more than $470 million per year.[70] This exceeds the entire 2023 antitrust budget for the FTC and DOJ combined.[71]
A. The Premerger Notification Form Risks Challenge as Arbitrary and Capricious
As an initial matter, the proposed changes clearly run contrary to legislative intent. As Chair Khan has herself noted, Congress expected only the 150 largest mergers each year would require notification to the agencies,[72] but the agencies today review several thousand reported transactions annually.[73] Former U.S. Rep. Peter Rodino, one of the authors of the HSR Act, anticipated that premerger notification would not entail the creation of new information and that compliance should not routinely delay consummation of deals.[74] Similarly, a “need to avoid burdensome notification requirements or fruitless delays”[75] was noted in the Senate. At least arguably, many of the NPRM’s proposed changes fail on all of these fronts.
Changes to the premerger notification process would carry to the force of law. So long as they are not arbitrary or capricious—and, usually, a failure to abide by the legislative history would not, in and of itself, surmount this bar—such changes are binding on parties to a merger. The hallmarks of arbitrary or capricious agency action were explained by the Supreme Court in State Farm:
Normally, an agency rule would be arbitrary and capricious if the agency has relied on factors which Congress has not intended it to consider, entirely failed to consider an important aspect of the problem, offered an explanation for its decision that runs counter to the evidence before the agency, or is so implausible that it could not be ascribed to a difference in view or the product of agency expertise.[76]
While the statute confers considerable discretion on the agencies’ implementation of the HSR Act’s amendments to the Clayton Act, that discretion is not unbounded. Indeed, there is good reason to believe that courts are likely to find many of the NPRM’s proposed changes to be arbitrary and capricious. The Act expressly limits the agencies to requiring production of information that is “relevant to a proposed acquisition as is necessary and appropriate . . . to determine whether such acquisition may, if consummated, violate the antitrust laws.”[77] And this text must be read in conjunction with the statutory authority to make second requests that “require the submission of additional information or documentary material relevant to the proposed acquisition.”[78] Moreover, any rules must be “consistent with the purposes of this section”—that is, to allow the antitrust agencies an opportunity to review significant mergers prior to their consummation to avoid the “unscrambling the egg” problem.
The statutory authority raises many textual questions. What constitutes “necessary” and “appropriate” information? And what does it mean for these words to be joined by the conjunction “and”? What is the extent of the limitation that information be “relevant to the proposed acquisition”? Is the “purpose of the section” limited to merger-related antitrust concerns, or more expansively related to the violation of any antitrust laws that might result from consummation of the transaction?[79] Each of these specify factors that Congress did or did not intend the agencies to consider or that may or may not be important aspects of the problem that Congress empowered the agencies to address.
Consider, for instance, what it means for materials to be “relevant to a proposed acquisition.” A natural reading would limit this to the materials that firms gathered in evaluating the transaction; and the submission of such extant materials would meet the ordinary meaning of “production” in a litigation context. The NPRM would expand the universe of relevant materials, including potentially anything that might inform a determination of the transaction’s legality. Courts are likely to say that the limit must be narrower than anything the agencies think potentially relevant to request.[80]
For example, the proposed rules would require disclosure of information about OSHA findings against the parties, on the theory that OSHA violations correlate with labor-market power. But as noted above, OSHA data suggest that the most common violations occur in industries that are minimally concentrated (e.g., construction). Similarly, the proposed rules would require parties to provide detailed information about the number of employees in broad categories working in overlapping commuting zones.[81] Such information might be useful in evaluating the competitive effects of a transaction,[82] but that utility is unclear. Furthermore, the information is not of a sort, or in a format, that parties to a merger are likely to compile in the ordinary course of business, or to aid themselves in deciding whether to pursue a merger. That is, from the parties’ perspective, this information would likely be irrelevant to a proposed acquisition, even if it might be relevant to the agencies’ evaluation of the effects of the proposed acquisition.
The point is underscored when considering the meaning of “necessary and appropriate.” As an initial matter—and echoing the concerns about information’s relevance to a proposed transaction— “appropriateness” could be determined with respect to purpose; that is, whether it is appropriate for the agencies to use the premerger notification process as a tool for developing novel theories of antitrust law or, in the alternative, whether it should be limited to screening for transactions that would violate established antitrust precedent under established methods.
“Necessary and appropriate” suggests an even more stringent constraint when read together. The availability of, and broad latitude afforded, second requests—among other tools, such as voluntary requests and “pull-and-refiles”—suggests that relatively little be required as part of the initial premerger notification. Indeed, without “and appropriate,” nothing would be required of a filing in the strict sense of “necessary,” as anything necessary might be gathered through a second request. Additional information is appropriate because it is both necessary to the process as a whole and appropriate to an initial filing by parties in general; that is, among other things, that it is not merger-specific information more efficiently gathered and screened with a proper subset of filers.
In addition, the burdens of required filing information (including those imposed by the HSR form) must be considered in light of the fact that the vast majority of mergers have not been deemed to raise competition concerns. Specifically, only 2% of all mergers subject to premerger notification receive second requests; and a second requests is not a complaint, much less a final decision that a proposed merger would be unlawful. That is, in considering the balance of what is reasonable and necessary, the agencies must be mindful of the fact that material required by HSR notification is a burden imposed on roughly 50 times the number of transactions as those deemed—in the agencies’ own judgment—to warrant a second request.
B. Problematic Premerger Notification Rules Might Escape Challenge
Were issues like these to be raised in a challenge to the premerger notification process, the outcome may be hard to predict, but a court could well decide against the agencies. Still, there is reason to worry, independent of the question of such a challenge in the courts. The costs of the premerger notification process act as a tax on transactions. And as a tax, it is a regressive one, most likely felt by firms considering transactions on the margin of the HSR-reporting thresholds. These may disproportionately affect firms that, while large enough to be subject to notification, are relatively small or relatively infrequent filers.
That points to a question about the relative burdens and benefits of the proposed changes, but it also suggests a question regarding when, or even whether, overly burdensome regulations are likely to be challenged in court. Because the burdens of the tax are spread across the thousands of firms engaged in HSR-reportable transactions each year, no single firm—or pair of firms—would have an incentive even remotely close to the economic cost of the rules; or to put it another way, because the costs of the rule would be spread over thousands of transactions, the incentives for any given firm (or pair of firms) to challenge the requirements would be a very small fraction of the economic burdens of the requirement as a whole.
While that might seem an advantage to the agencies—at least insofar as the agencies might be concerned about litigation risk—it is not an advantage to efficient rulemaking or, specifically, to rules that provide for effective premerger screening without placing undue burdens on procompetitive or benign transactions.
In brief, the tax imposed by the new process would be imposed across a very large number of lawful mergers, including (and, very largely, comprising) mergers that would benefit both competition and consumers. As a regressive tax, it would also likely have an outsized effect on transactions at the margin of the HSR-reporting thresholds; and these may be those transactions least likely to raise competition concerns or lead to an agency challenge.
VII. Conclusion
Certain proposed changes to the HSR-reporting rules and form may be necessary. For example, the NPRM’s proposed changes to Part 801.1 of the HSR rules appears to be a reasonable implementation of the 2022 statutory amendments to the Clayton Act that require the disclosure of subsidies from nations or entities that Congress has identified as “foreign entities of concern.”[83]
In addition, as we have also discussed, the NPRM’s proposal to amend Part 803 to require electronic filing[84] will likely be salutary, especially with the successful implementation of an e-filing platform that, according to the NPRM, is under development.[85] Electronic production and merger screening is in widespread use already, and more comprehensive adoption and standardization of electronic filing should help streamline premerger screening for both filers and the agency staff charged to review filings.
Many other proposals in the NPRM would greatly increase compliance costs for merging parties generally, with disproportionate impact on small and first-time filers. They would, not incidentally, also impose additional burdens on the agency staff who are charged to screen such mergers. Yet the screening value of much of the information is entirely unclear. For example, the NPRM proposes to require the production of considerable information about violations of labor regulations—such as OSHA regulations regarding worker safety—that have no evident connection (or even correlation) with highly concentrated product or labor markets, much less a demonstrated connection with harm to competition and consumers. Similarly, the utility of new information bundling industry “overlaps” based on six-digit occupational codes (not labor markets) and Department of Commerce “commuting zones” (not necessarily the geographic component of labor markets, either) is unclear.
Further enforcement experience with labor-market competition matters, and further empirical investigation, could develop such that the inclusion of additional labor information in the filing requirements would be reasonable and necessary. But such developments should precede, not follow, the formulation and imposition of such requirements. In the absence of such developments, it seems highly unlikely that the costs of the new requirements would be offset by countervailing benefits to competition and consumers.
By the NPRM’s own estimate, those costs are substantial. And the NPRM’s estimate seems extremely low, given the considerable time that senior executives and firm counsel would need to devote to compliance. Moreover, the costs of the new rules would work as a regressive tax, tending to chill mergers by smaller and less frequently transacting firms. Most of the mergers chilled by such costs would likely be—like the vast majority of mergers—either procompetitive or benign. Impeding them would thus be to the detriment—not the protection—of competition and consumers.
Finally, such costs would be imposed on all firms required to file HSR notifications, notwithstanding other means of gathering screening information, and notwithstanding that fewer than 2% of reported transactions lead even to a “second request.” Given the high and skewed costs of the proposals, and given the statutory charge to collect only information that is necessary and reasonable, many of the proposed changes seem not only unnecessary, cumbersome, and costly, but in excess of the rulemaking authority conferred by the HSR Act’s amendments to the Clayton Act.
For these reasons, we urge the commission to consider seriously the evidentiary bases of its proposed changes to the HSR rules and to scale back its proposal accordingly.
[1] Premerger Notification Rules, 88 Fed. Reg. 42178 (RIN 3084-AB46), proposed Jun. 29, 2023) (to be codified at 16 C.F.R. Parts 801 and 803) [hereinafter “NPRM”].
[2] See generally, e.g., William E. Kovacic & Carl Shapiro, Antitrust Policy: A Century of Economic and Legal Thinking, 14 J. Econ. Persp. 43 (2000).
[3] Statement of Chair Lina M. Khan, Commissioner Rohit Chopra, and Commissioner Rebecca Kelly Slaughter on the Withdrawal of the Vertical Merger Guidelines, Fed. Trade Comm’n, Commission File No. P810034 (Sep. 15, 2021), available at https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/documents/public_statements/1596396/statement_of_chair_lina_m_khan_commissioner_rohit_chopra_and_commissioner_rebecca_kelly_slaughter_on.pdf (citing Open Markets Inst. et al., Comment Letter No. 31 on #798: Draft Vertical Merger Guidelines (“Draft VMGs”), Matter No. P810034 at 4 (Feb. 2020)).
[4] 15 U.S.C. § 18a(d)-(e).
[5] Id. at (d)(1).
[6] 15 U.S.C. § 46(b).
[7] Draft Merger Guidelines, U.S. Dep’t Justice & Fed. Trade Comm’n, Document No. FTC-2023-0043-0001 (Jul. 19, 2023), https://www.regulations.gov/document/FTC-2023-0043-0001. For comments on the draft merger guidelines see, e.g., Comment from International Center for Law & Economics, FTC-2023-0043-1555 (Sep. 18, 2023), https://www.regulations.gov/comment/FTC-2023-0043-1555; Comments of Economists and Lawyers on the Draft Merger Guidelines, FTC-2023-0043-1406 (Sep. 15, 2023), https://www.regulations.gov/comment/FTC-2023-0043-1406; Comment from Gregory J. Werden, FTC-2023-0043-0624 (Aug. 12, 2023), https://www.regulations.gov/comment/FTC-2023-0043-0624; Comment from Professor Carl Shapiro, FTC-2023-0043-1393 (Sep. 14, 2023), https://www.regulations.gov/comment/FTC-2023-0043-1393; Comment from Global Antitrust Institute, FTC-2023-0043-1397 (Sep. 14, 2023), https://www.regulations.gov/comment/FTC-2023-0043-1397; Comment from Compass Lexecon, FTC-2023-0043-1518 (Sep. 18, 2023), https://www.regulations.gov/comment/FTC-2023-0043-1518; Comment from Herbert Hovenkamp, FTC-2023-0043-1280 (Sep. 8, 2023), https://www.regulations.gov/comment/FTC-2023-0043-1280.
[8] Id.
[9] Or 15 days, in the case of tender offers. 15 U.S.C. § 18(b)(1)(B), (e)(1)(A).
[10] See, e.g., Lina Khan, Chair, FTC and Jonathan Kanter, Asst. Atty. Gen., Antitrust Div., Hart-Scott-Rodino Annual Report, Fiscal Year 2021, 4 (2023), available at https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/ftc_gov/pdf/p110014fy2021hsrannualreport.pdf.
[11] 15 USC § 18a(e)(1)(A); Cf., Hart-Scott-Rodino Annual Report, Fiscal Year 2021, Appendix A, U.S. Dep’t Justice & Fed. Trade Comm’n (2023), available at https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/ftc_gov/pdf/p110014fy2021hsrannualreport.pdf (summary of reported transactions by fiscal year, 2012-2021, showing, inter alia, percentage of filings leading to second requests).
[12] 15 USC § 18a(e)(2).
[13] See, e.g., Statement of Representative Rodino, Merger Oversight and H.R. 13131, Providing Premerger Notification and Stay Requirements, Subcomm. on Monopolies and Commercial Law of the Comm. on the Judiciary (Mar. 10, May 6 and 13, 1976) (“Both agencies can, and will, tell us what we have known for years—you can’t unscramble an egg.”).
[14] See Statement of Federal Trade Commission Chair Khan, Joined by Commissioner Rebecca Kelly Slaughter and Commissioner Alvaro M. Bedoya, Regarding Proposed Amendments to the Premerger Notification Form and the Hart-Scott-Rodino Rules, at 2 (Jun. 27, 2023), available at https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/ftc_gov/pdf/statement_of_chair_khan_joined_by_commrs_slaughter_and_bedoya_on_the_hsr_form_and_rules_-_final_130p_1.pdf.
[15] Id.; see also Annual Reports to Congress Pursuant to the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act of 1976, Fed. Trade Comm’n (2021), https://www.ftc.gov/policy/reports/annual-competition-reports.
[16] E.g., Joe Simms, The Effect of Twenty Years of Hart-Scott-Rodino on Merger Practice: A Case Study in the Law of Unintended Consequences Applied to Antitrust Legislation, 65 Antitrust L.J. 865 (1997).
[17] The FTC’s introductory guide to the premerger process, for instance, says of the process that: “The Program has been a success.” What is the Premerger Notification Program? An Overview, Fed. Trade Comm’n (Mar. 2009), available at https://www.ftc.gov/sites/default/files/attachments/premerger-introductory-guides/guide1.pdf. This is not to say that the program is without critics or criticism. The initial implementation, for instance, did not index reporting thresholds to inflation. By the year 2000, nearly 5,000 transactions were noticed each year. The HSR Act was subsequently amended to index thresholds to inflation. Today, roughly 2,000 transactions are noticed each year (allowing for some variation during the pandemic). See Fed. Trade Comm’n, supra note 22, available at https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/ftc_gov/pdf/p110014fy2021hsrannualreport.pdf. See also Report of the Antitrust Modernization Committee, 158 (“the existing pre-merger review system under the HSR Act is achieving its intended objectives of providing a more effective means for challenging mergers raising competitive concerns before their consummation and protecting consumers from anticompetitive effects.”), available at https://govinfo.library.unt.edu/amc/report_recommendation/amc_final_report.pdf.
[18] Andrew G. Howell, Why Premerger Review Needed Reform-and Still Does, 43 Wm. & Mary L. Rev. 1703, 1716 (2002) (“There are several key points to draw from this legislative history. First, the premerger title of the Act was meant only to make the procedural change of requiring notification—it was not meant to change substantive law. Second, the provision was intended to encompass only the very largest of mergers. Finally, there was concern in Congress about not allowing pursuit of merger enforcement goals to place too much of a burden on commerce.”)
[19] Premerger Notification; Reporting and Waiting Period Requirements, 85 Fed. Reg. 77042, 77055 (RIN 3084-AB46), proposed Dec. 1, 2020 (to be codified at 16 C.F.R. Parts 801, 802, and 803)
[20] Hart-Scott-Rodino Annual Report, Fiscal Year 2021, supra note at 1-2.
[21] Id. at Appendix (A summary of reported transactions by fiscal year, 2012-2021, showing, inter alia, percentage of filings leading to second requests).
[22] The difference may, of course, be greater still, given the nature of a second request. Based on the initial filing and follow-up information, the agencies have very broad discretion in seeking additional production via a second request; at the same time, we understand that staff tend not to request additional information by rote, but according to merger-specific concerns and queries.
[23] Antitrust Experts Reject FTC/DOJ Changes to Merger Process, U.S. Chamber of Commerce (Sep. 19, 2023), https://www.uschamber.com/finance/antitrust/antitrust-experts-reject-ftc-doj-changes-to-merger-process. The surveyed group was made up seasoned antitrust veterans from across a variety of backgrounds: 80% had been involved in more than 50 mergers and 59% in more than 100.
[24] Id. at 2.
[25] Id. at 3.
[26] NPRM at 42208.
[27] We note, however, that both the NPRM and the draft merger guidelines suggest a greatly expanded notion of “overlaps,” adding to the likely costs to filers and, not incidentally, burden to reviewing staff.
[28] See, e.g., HSR Statements of Basis and Purpose, FTC Legal Library, https://www.ftc.gov/legal-library/browse/hsr-statements-basis-purpose (last checked Sep. 23, 2023).
[29] For example, year 2000 amendments to the HSR Act required annual publication of adjustments to the Act’s jurisdictional and filing-fee thresholds in the Federal Register for each fiscal year, beginning Sept. 30, 2004, based on change in the gross national product, in accordance with Section 8(a)(5) of the Clayton Act.
[30] Revised Jurisdictional Thresholds, 88 Fed. Reg. 5004 (Jan. 26, 2023).
[31] Revised Jurisdictional Thresholds for Section 7A of the Clayton Act, 87 Fed. Reg. 3541 (Jan. 24, 2022).
[32] Revised Jurisdictional Thresholds for Section 7A of the Clayton Act, 86 Fed. Reg. 7870 (Feb. 2, 2021).
[33] Premerger Notification; Reporting and Waiting Period Requirements, 85 Fed. Reg. 77042 (RIN 3084-AB46), proposed Dec. 1, 2020 (to be codified at 16 C.F.R. Parts 801, 802, and 803).
[34] NPRM at 42180-81 (discussing provisions of the Merger Filing Fee Modernization Act of 2022, Pub. L. 117-328, 136 Stat. 4459 (2022), Div. GG.).
[35] Id.
[36] NPRM at 42181.
[37] Id. at 42180.
[38] Id. at 42181.
[39] Antitrust Improvements Act Notification and Report Form for Certain Mergers and Acquisitions: Instructions, available at https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/ftc_gov/pdf/HSRFormInstructions02.27.23.pdf.
[40] NPRM at 42191.
[41] David C. Kully, et al., Killing Deals Softly: FTC Proposes 107-Hour Increase in Hart-Scott-Rodino Burden, Holland & Knight Alert (Jun. 28, 2023), https://www.hklaw.com/en/insights/publications/2023/06/killing-deals-softly-ftc-proposes-107-hour-increase.
[42] NPRM at 42193
[43] Id. at 42196.
[44] Id. at 42197.
[45] Id. at 42196-42197.
[46] Id. at 42197.
[47] 15 U.S.C. § 18a(e)(1)-(2).
[48] Statement of Commissioner Alvaro M. Bedoya, Joined by Chair Lina M. Khan and Commissioner Rebecca Kelly Slaughter Regarding the Proposed Merger Guidelines, U.S. Dep’t Justice & Fed. Trade Comm’n (Jul. 19, 2023), available at https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/ftc_gov/pdf/p234000_merger_guidelines_statement_bedoya_final.pdf (internal citations omitted, but including a reference to FTC, Non-HSR Reported Acquisitions by Select Technology Platforms, 2010-2019 (Sept. 15, 2021), https://www.ftc.gov/reports/non-hsr-reported-acquisitions-select-technology-platforms-2010-2019-ftc-study.)
[49] Id. at 3.
[50] Ginger Zhe Jin, Mario Leccese, & Liad Wagman, How Do Top Acquirers Compare in Technology Mergers? New Evidence from an S&P Taxonomy, 89 J. Indus. Org. (2023), https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/ S0167718722000662.
[51] Id.
[52] NPRM at 42197.
[53] Id. at 42197-98.
[54] Id.
[55] Id. at 42198.
[56] NPRM at 42198, 42215.
[57] Id.
[58] Id.
[59] Top 10 Most-cited Standards for Fiscal Year 2022, U.S. Dep’t Labor, Occupational Safety & Health Admin., https://www.osha.gov/top10citedstandards. The source page includes a link to a searchable database of Frequently Cited OSHA Standards by industry.
[60] 15 U.S.C. § 18a.
[61] Id.
[62] 15 U.S.V. § 18a(d).
[63] 5 U.S.C. § 553.
[64] Id.
[65] Motor Vehicle Mfrs. Ass’n of U.S., Inc. v. State Farm Mut. Auto. Ins. Co., 463 U.S. 29 (1983).
[66] See A Guide to the Rulemaking Process, Office of the Federal Register (Jan. 2011), available at https://www.federalregister.gov/uploads/2011/01/the_rulemaking_process.pdf. In addition, regulations may be constitutionally infirm.
[67] The FTC’s 2023 budget request for antitrust enforcement (“Promoting Competition”) was $239,613,000. See Fiscal Year 2023 Congressional Budget Justification, Fed. Trade Comm’n (Mar. 28, 2022), available at https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/ftc_gov/pdf/P859900FY23CBJ.pdf. The Department of Justice’s similar request 2023 appropriation was $225,000,000. See Appropriation Figures for The Antitrust Division, Fiscal Years 1903-2023, Dep’t of Just., Antitrust Div (Feb. 2023), https://www.justice.gov/atr/appropriation-figures-antitrust-division.
[68] Id. at 42198.
[69] To demonstrate the need for information about labor market conditions in evaluating mergers, the NPRM identifies only two recent (2021 and 2022) decisions by the agencies to bring actions against firms that include labor-market concerns. Id. at 42197.
[70] NPRM at 42208 (“the total estimated additional hours burden is 759,272. . . . Applying the revised estimated hours, 759,272, to the previous assumed hourly wage of $460 for executive and attorney compensation, yields approximately $350,000,000 in labor costs.”).
[71] The FTC’s 2023 budget request for antitrust enforcement (“Promoting Competition”) was $239,613,000. See Fed. Trade Comm’n, Fiscal Year 2023 Congressional Budget Justification, https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/ftc_gov/pdf/P859900FY23CBJ.pdf. The Department of Justice’s similar request 2023 appropriation was $225,000,000. See Dep’t of Just., Antitrust Div., Appropriation Figures for The Antitrust Division, Fiscal Years 1903-2023 (Feb. 2023), https://www.justice.gov/atr/appropriation-figures-antitrust-division.
[72] See Statement of Federal Trade Commission Chair Khan, supra note 15, at 2.
[73] See Hart-Scott-Rodino Annual Report, Fiscal Year 2021, supra note 11, at 1 (noting 3,520 transactions for fiscal year 2021).
[74] Rep. Rodino himself indicated: “Government requests for additional information must be reasonable. [. . .] the Government will be requesting the very data that is already available to the merging parties, and has already been assembled and analyzed by them. If the merging parties are prepared to rely on it, all of it should be available to the Government. But lengthy delays and extended searches should consequently be rare.”
[75] S. Rep. No. 94-803, pt. 1, at 65, 67 (1976) (“A proper balance should exist between the needs of effective enforcement of the law and the need to avoid burdensome notification requirements or fruitless delays.”)
[76] 463 U.S. at 43.
[77] 15 U.S.C. § 18a(d).
[78] Id. at § 18a(e)(1).
[79] Strictly merger-related concerns would be limited to those that violate Section 7 of the Clayton Act (that is, consummation of transactions where the effect “may be substantially to lessen competition, or to tend to create a monopoly.”) Other concerns that might result from the transaction, such as an interlocking directorate prohibited by Section 8 of the Clayton Act, might therefore be excluded.
[80] See, e.g., AT&T Corp. v. Iowa Utils Bd, 525 U.S. 1133 (1999) (“the Act requires the FCC to apply some limiting standard, rationally related to the goals of the Act, which it has simply failed to do.”)
[81] NPRM at 42198.
[82] Given the coarseness of the data requested, it is doubtful whether it would be analytically useful for such purposes.
[83] NPRM at 42180-81.
[84] Id. at 42181.
[85] Id. at 42180.









